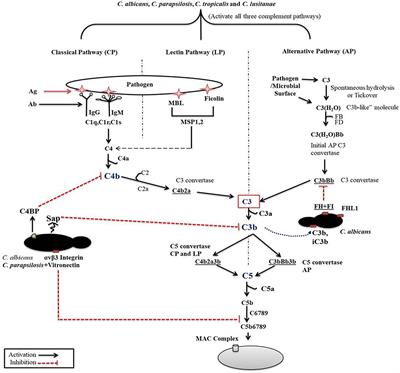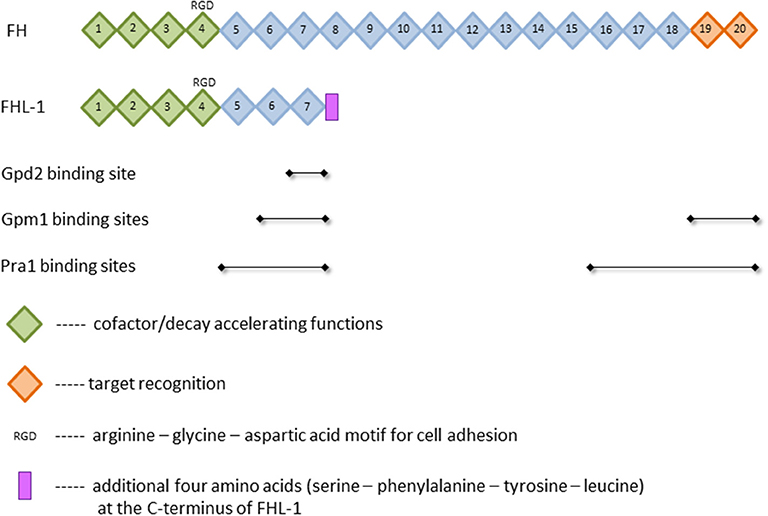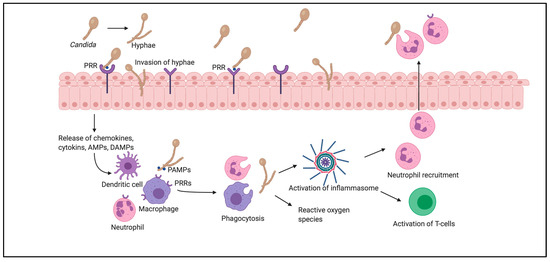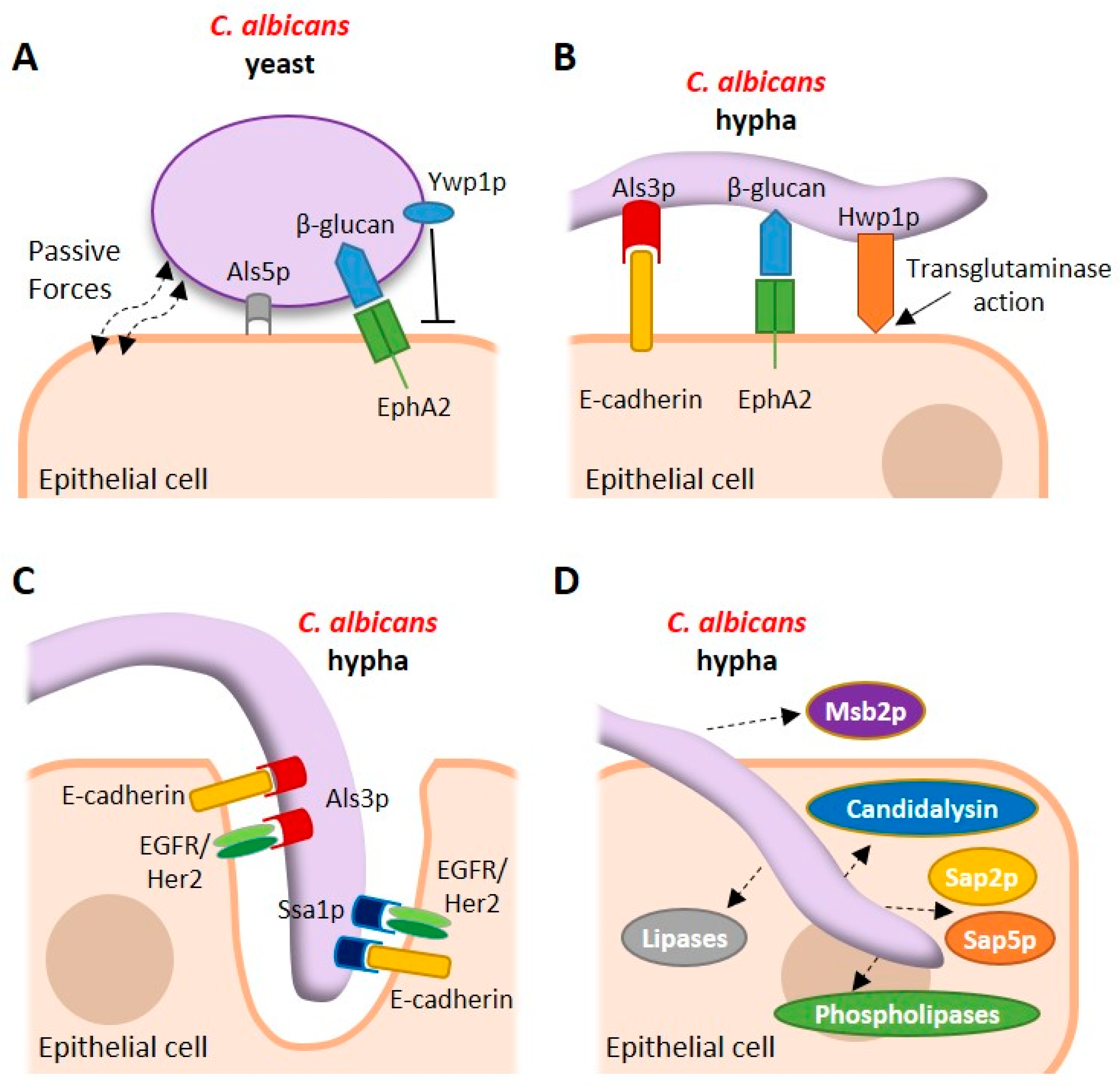
Pathogens | Free Full-Text | Candida albicans Interactions with Mucosal Surfaces during Health and Disease
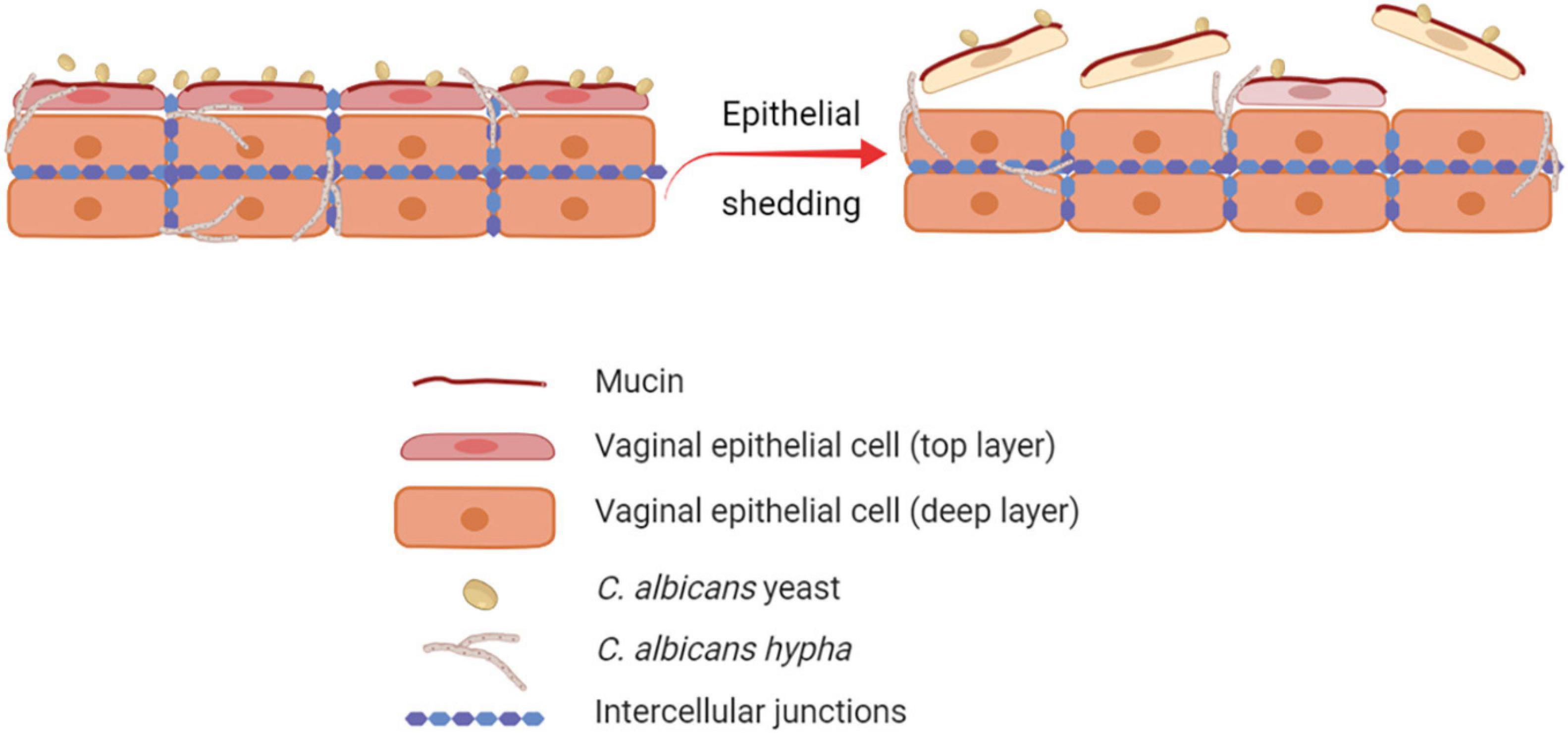
Frontiers | It Takes Two to Tango: How a Dysregulation of the Innate Immunity, Coupled With Candida Virulence, Triggers VVC Onset
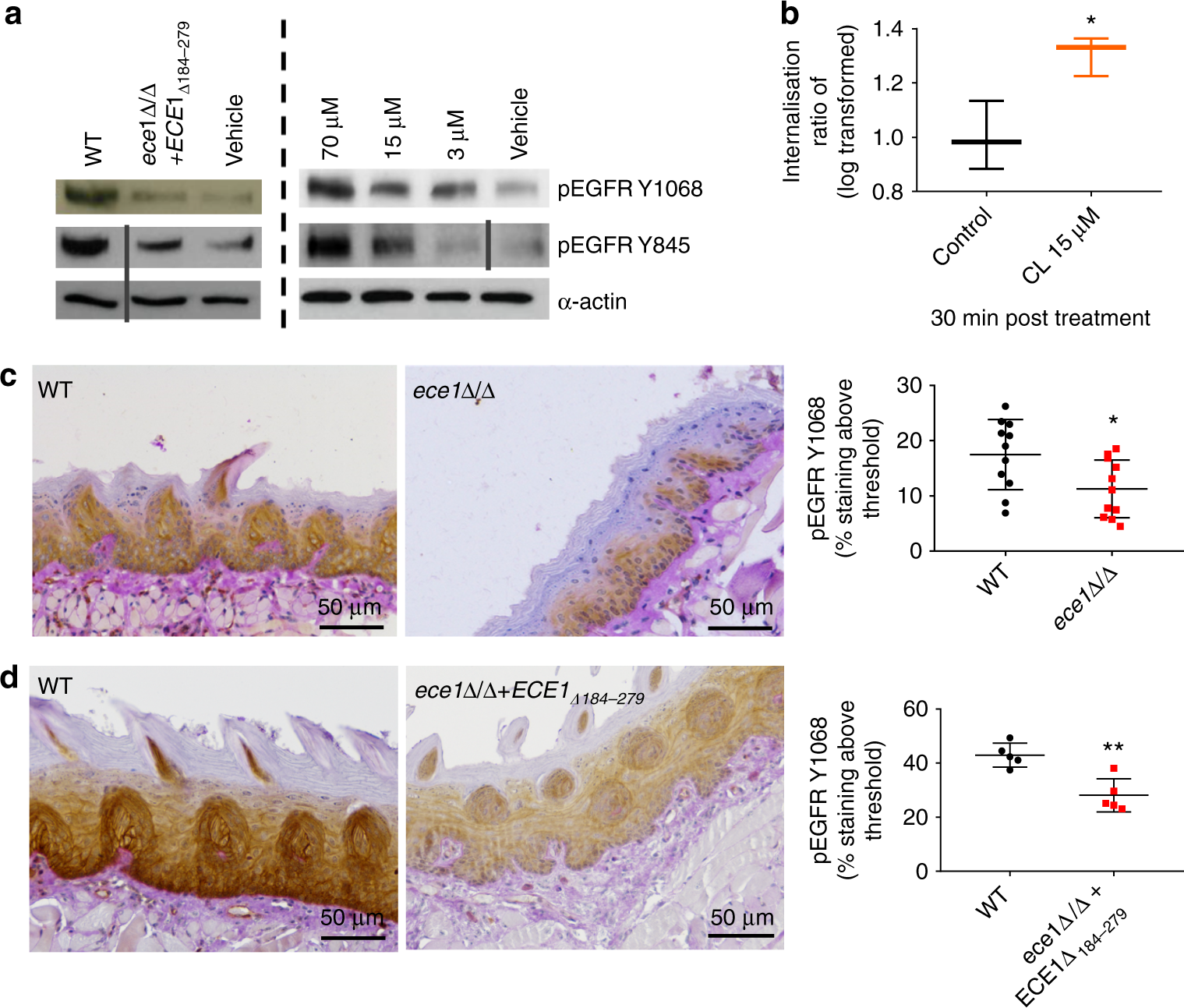
Candidalysin activates innate epithelial immune responses via epidermal growth factor receptor | Nature Communications

Global Secretome Characterization of the Pathogenic Yeast Candida glabrata | Journal of Proteome Research

Interactions of Candida albicans with host epithelial cells. (A) C.... | Download Scientific Diagram
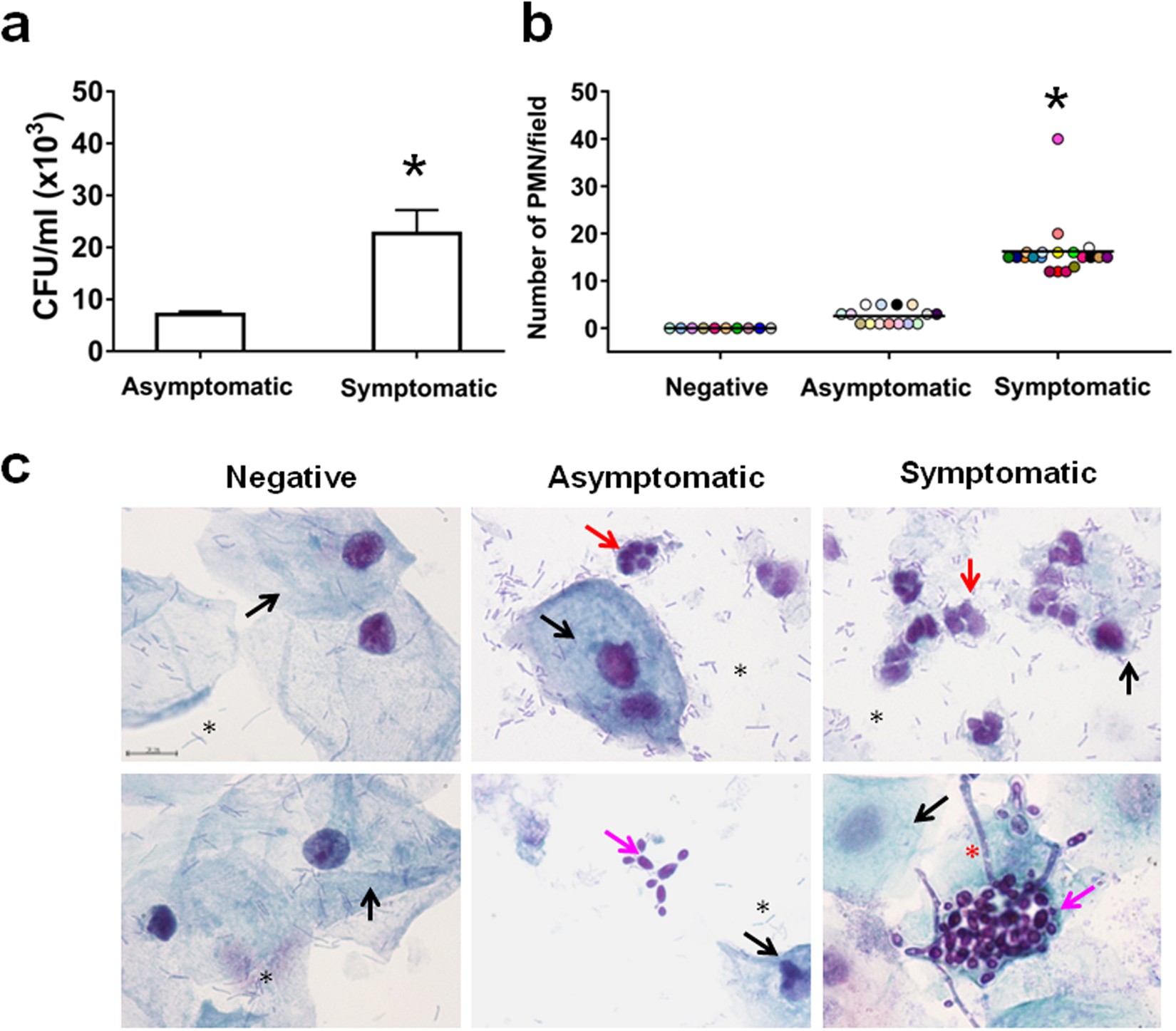
NLRP3 inflammasome is a key player in human vulvovaginal disease caused by Candida albicans | Scientific Reports

Immunoelectron microscopy (IEM). Detection of Sap3 in pleomorphic cells... | Download Scientific Diagram
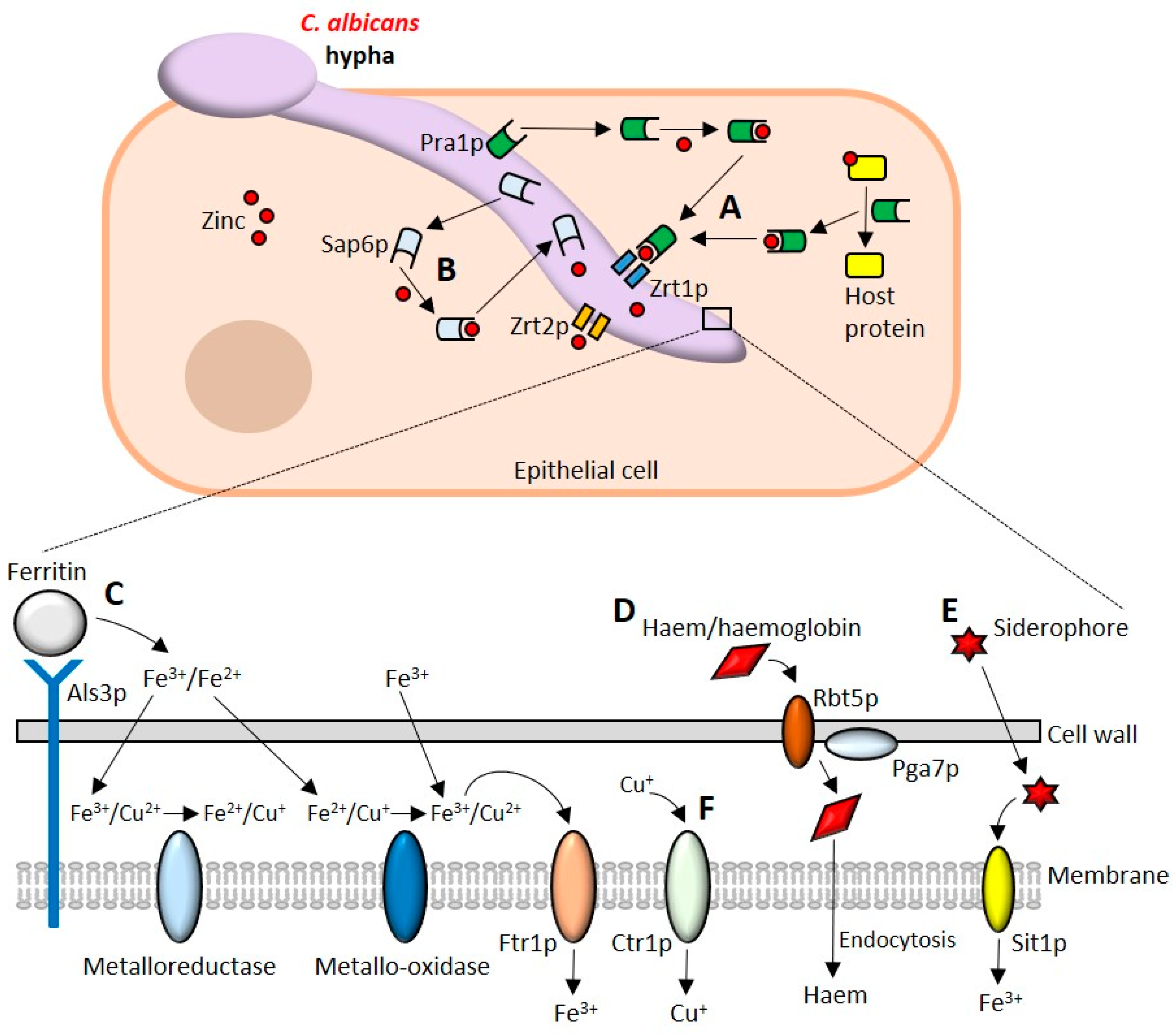
Pathogens | Free Full-Text | Candida albicans Interactions with Mucosal Surfaces during Health and Disease

Frontiers | Aspartic Proteases and Major Cell Wall Components in Candida albicans Trigger the Release of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps

In vivo PMN chemotactic ability of culture supernatants containing C.... | Download Scientific Diagram
Human Epithelial Cells Discriminate between Commensal and Pathogenic Interactions with Candida albicans | PLOS ONE
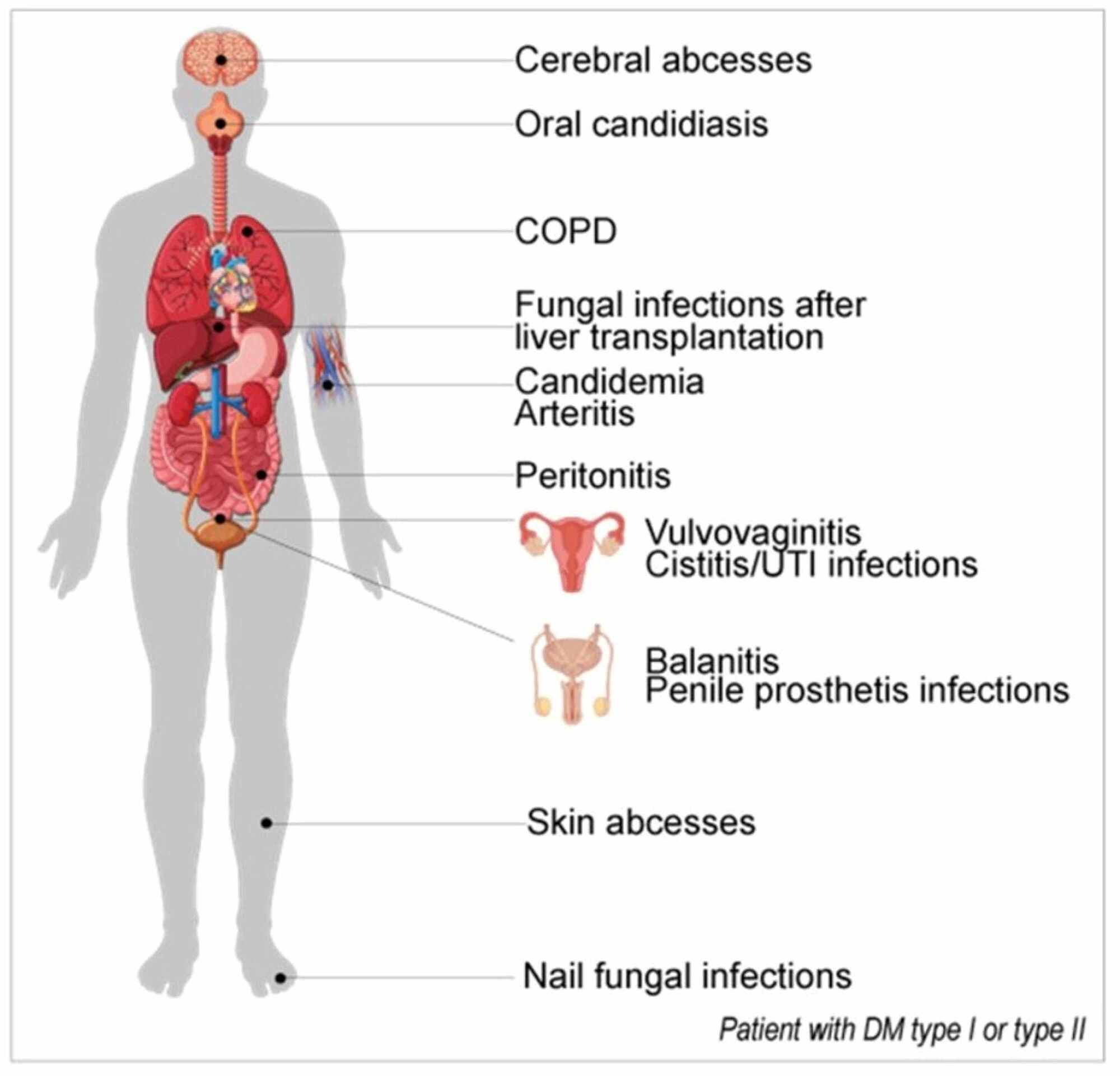
Cureus | The Interplay Between Sugar and Yeast Infections: Do Diabetics Have a Greater Predisposition to Develop Oral and Vulvovaginal Candidiasis? | Article