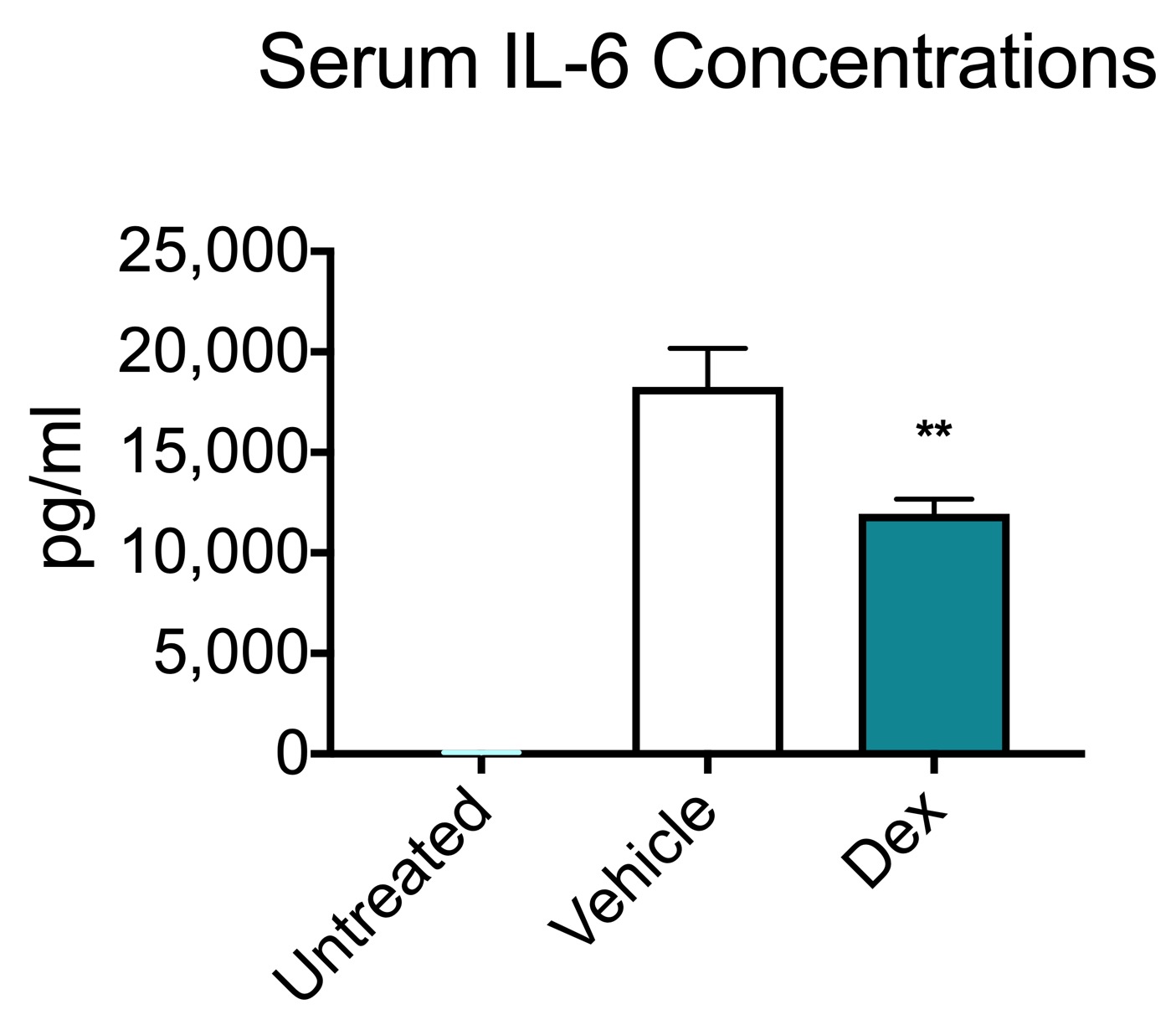
Suppression of LPS-induced inflammatory responses by the hydroxyl groups of dexamethasone | Oncotarget
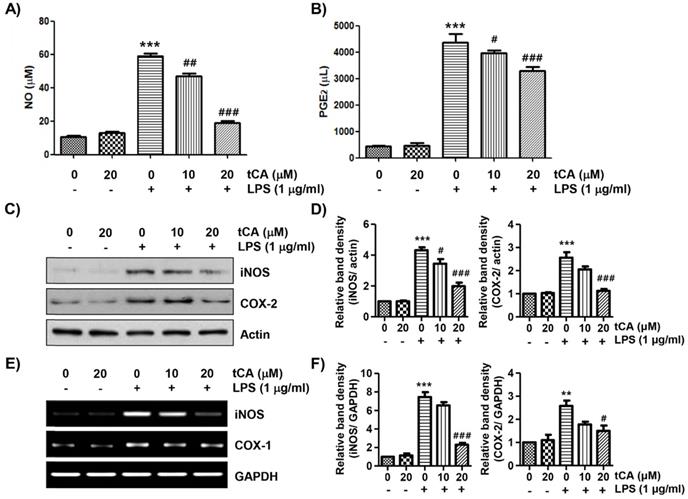
Inhibition of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory and Oxidative Responses by Trans-cinnamaldehyde in C2C12 Myoblasts

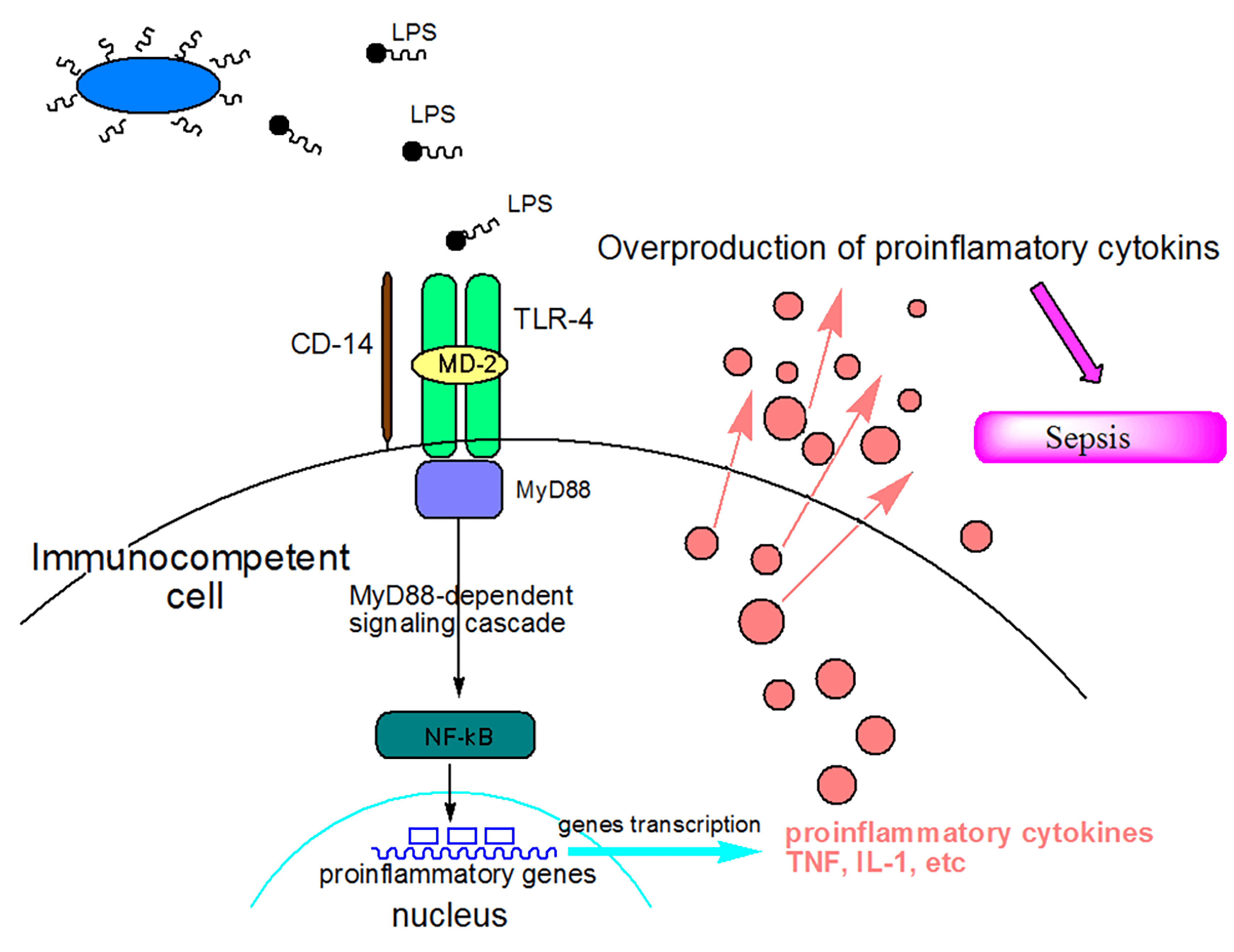
Human lipopolysaccharide models provide mechanistic and therapeutic insights into systemic and pulmonary inflammation | European Respiratory Society
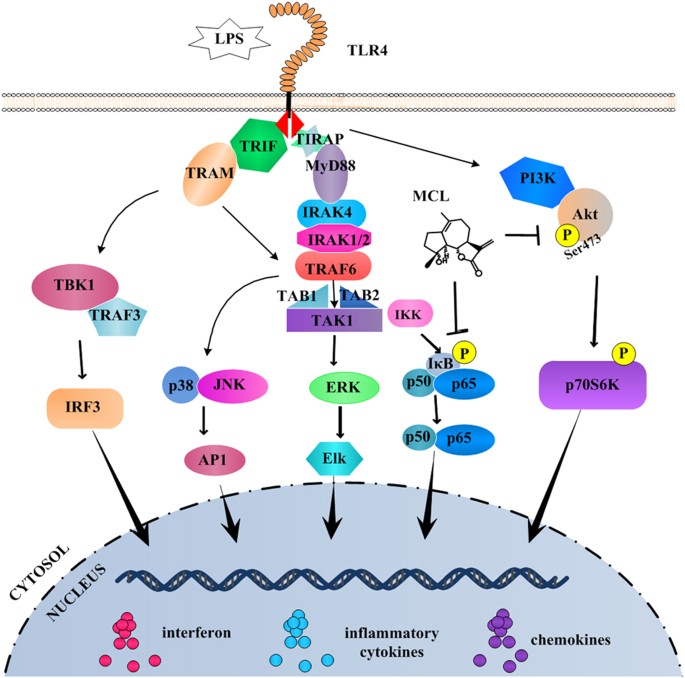
Micheliolide inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response and protects mice from LPS challenge | Scientific Reports
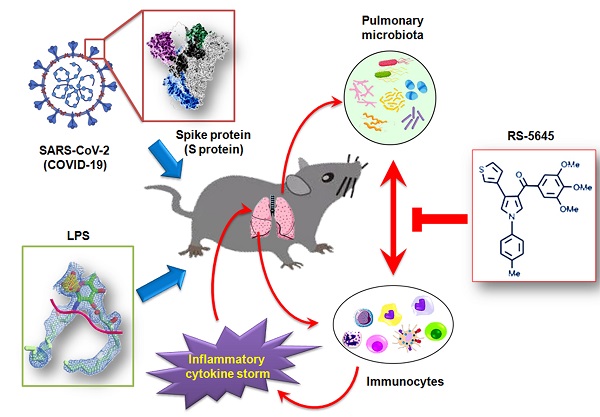
RS-5645 attenuates inflammatory cytokine storm induced by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and LPS by modulating pulmonary microbiota
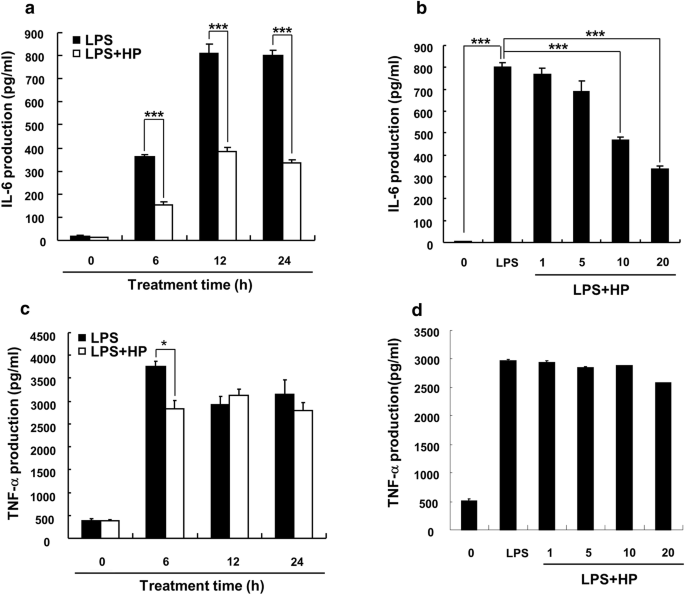
Anti-inflammatory effect of hispidin on LPS induced macrophage inflammation through MAPK and JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathways | Applied Biological Chemistry | Full Text

Single-cell secretion analysis reveals a dual role for IL-10 in restraining and resolving the TLR4-induced inflammatory response | bioRxiv
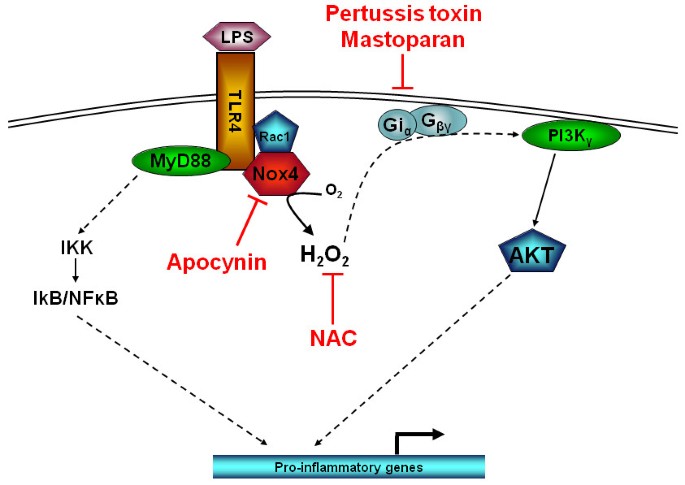
LPS induced inflammatory responses in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells is mediated through NOX4 and Giα dependent PI-3kinase signalling | Journal of Inflammation | Full Text

Alveolar macrophage phagocytic activity is enhanced with LPS priming, and combined stimulation of LPS and lipoteichoic acid synergistically induce pro-inflammatory cytokines in pigs - Mohammad Ariful Islam, Maren Pröll, Michael Hölker, Ernst
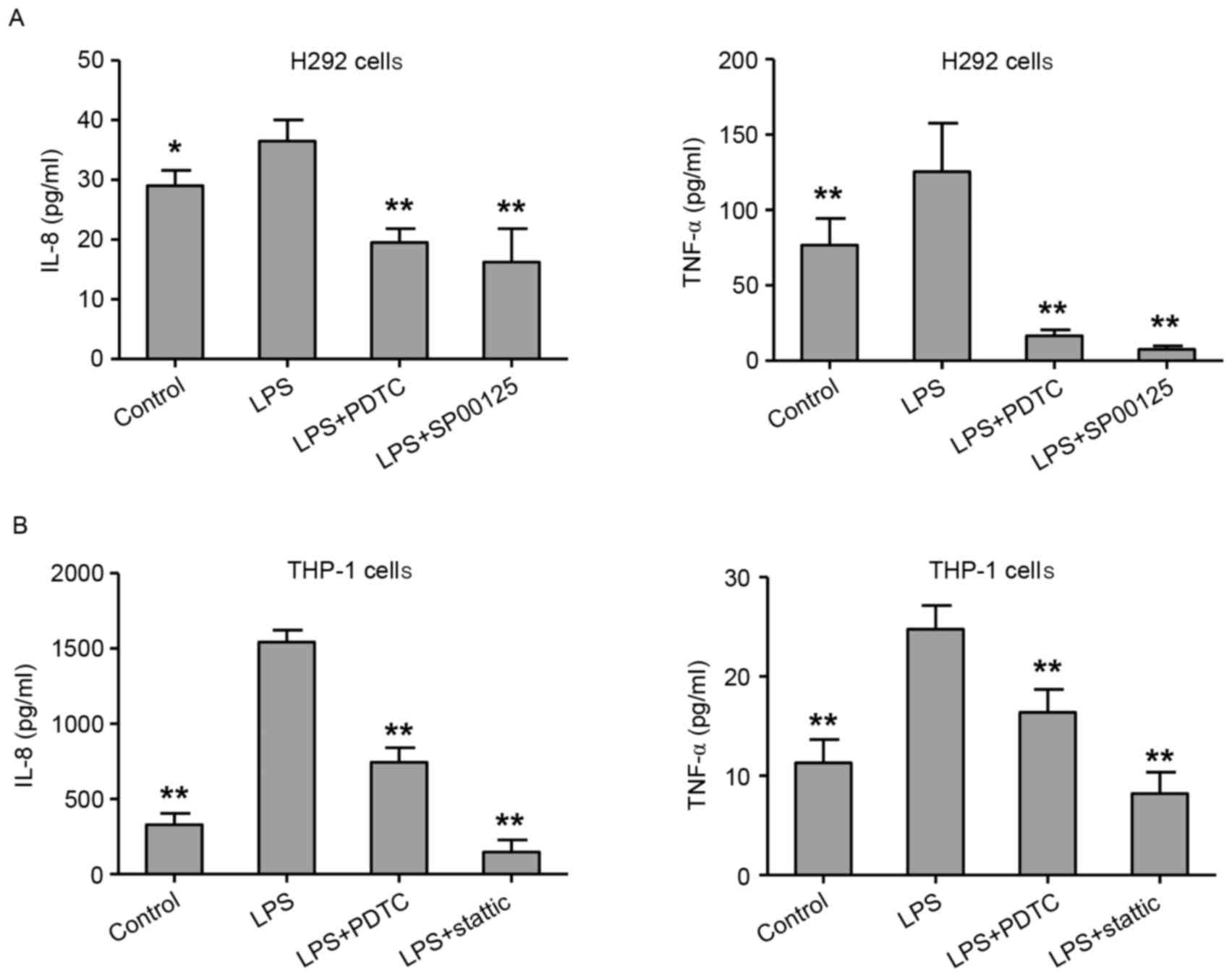
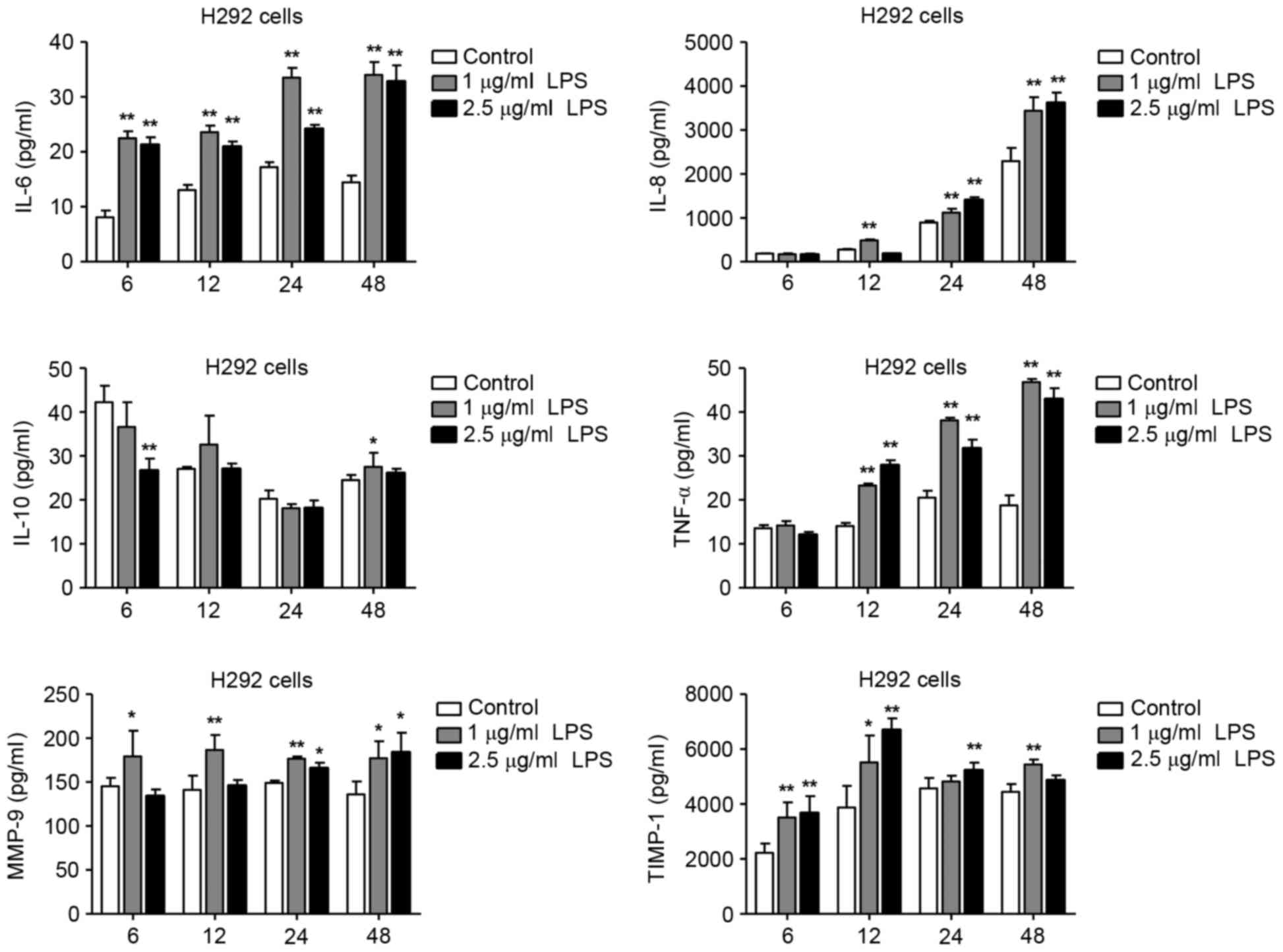
LPS‑induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF‑κB, STAT3 or AP‑1 activation

Bavachin attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory response and inhibits the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages - ScienceDirect

Noncanonical STAT1 phosphorylation expands its transcriptional activity into promoting LPS-induced IL-6 and IL-12p40 production | Science Signaling
Lipopolysaccharide-driven Th2 Cytokine Production in Macrophages Is Regulated by Both MyD88 and TRAM*
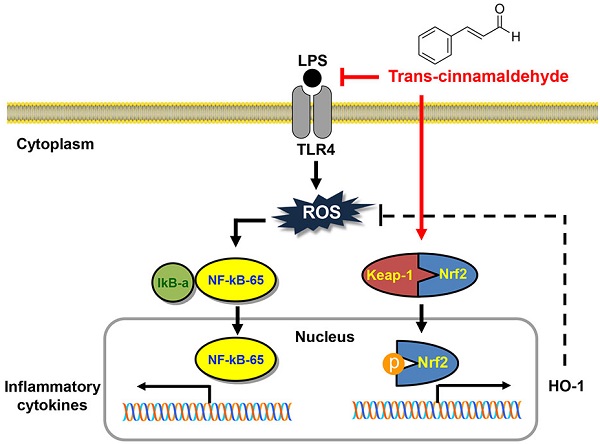
Inhibition of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory and Oxidative Responses by Trans-cinnamaldehyde in C2C12 Myoblasts

Methane limit LPS-induced NF-κB/MAPKs signal in macrophages and suppress immune response in mice by enhancing PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β-mediated IL-10 expression | Scientific Reports
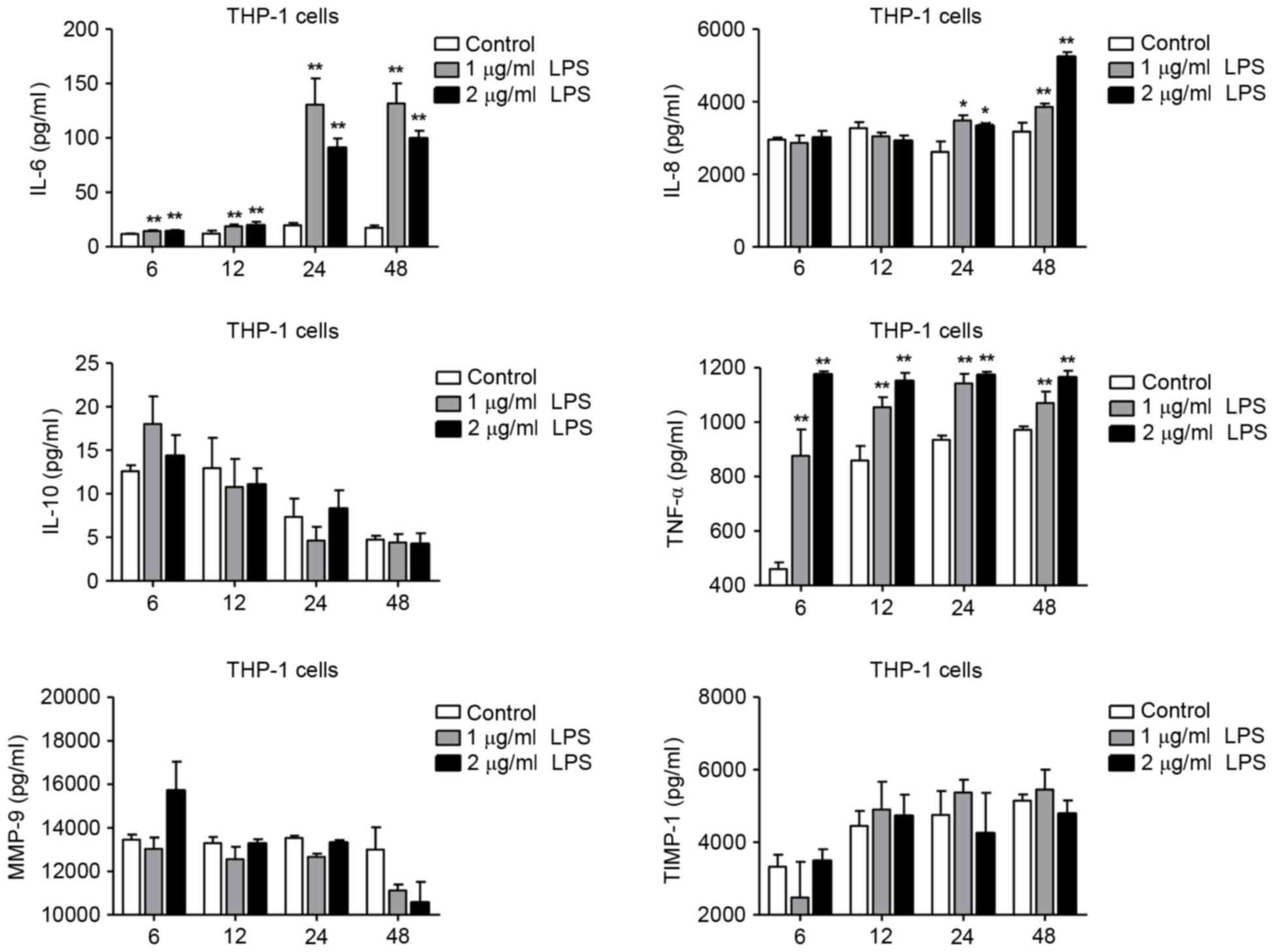
LPS‑induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF‑κB, STAT3 or AP‑1 activation

Imoxin attenuates LPS‐induced inflammation and MuRF1 expression in mouse skeletal muscle - Valentine - 2018 - Physiological Reports - Wiley Online Library

LPS-induced TNF-α factor (LITAF)-deficient mice express reduced LPS-induced cytokine: Evidence for LITAF-dependent LPS signaling pathways | PNAS
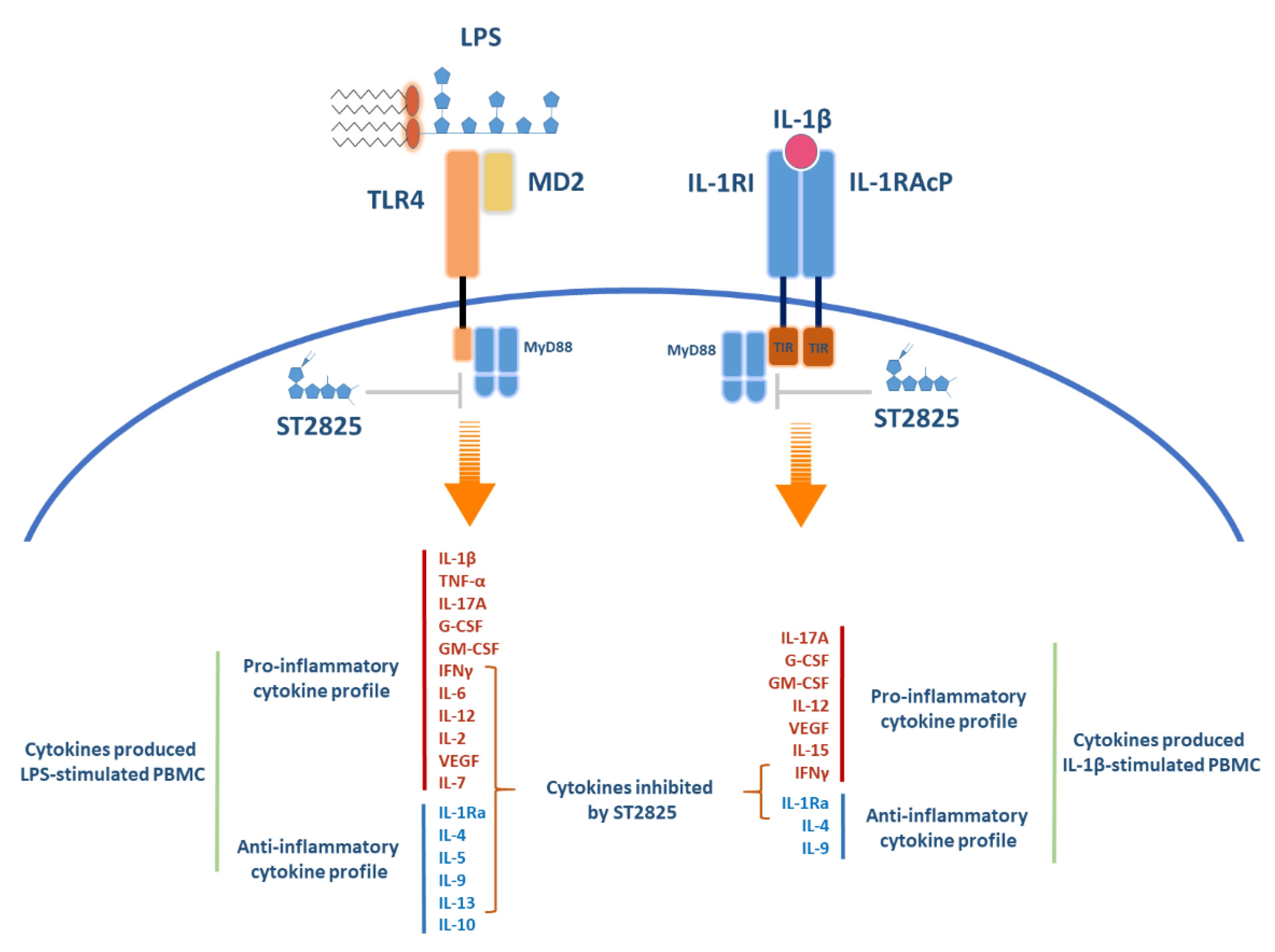
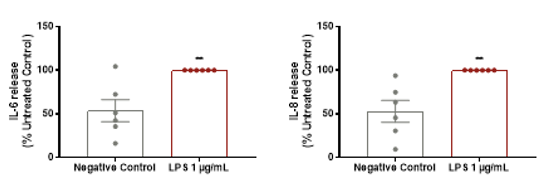
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Downregulation of Inflammatory Cytokine Release from IL-1β and LPS-Stimulated PBMC Orchestrated by ST2825, a MyD88 Dimerisation Inhibitor