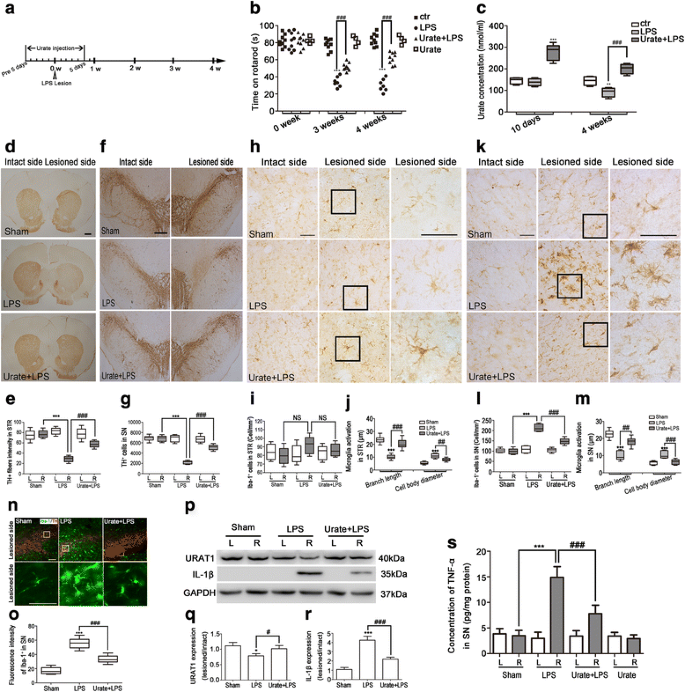
Urate inhibits microglia activation to protect neurons in an LPS-induced model of Parkinson's disease | Journal of Neuroinflammation | Full Text

PDF) Effects of Adenosine Receptor Antagonists on the In Vivo LPS-Induced Inflammation Model of Parkinson's Disease | Jadwiga Wardas - Academia.edu
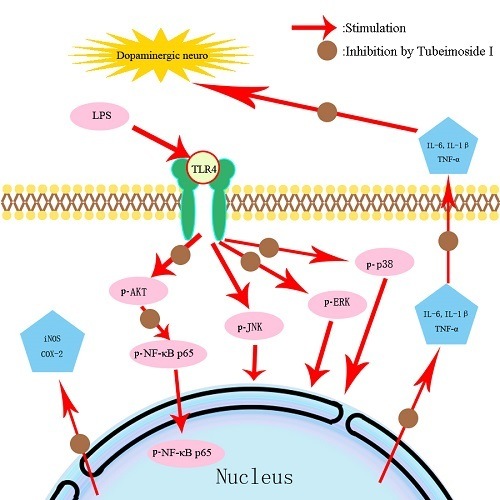
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Tubeimoside I Protects Dopaminergic Neurons Against Inflammation-Mediated Damage in Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Evoked Model of Parkinson's Disease in Rats
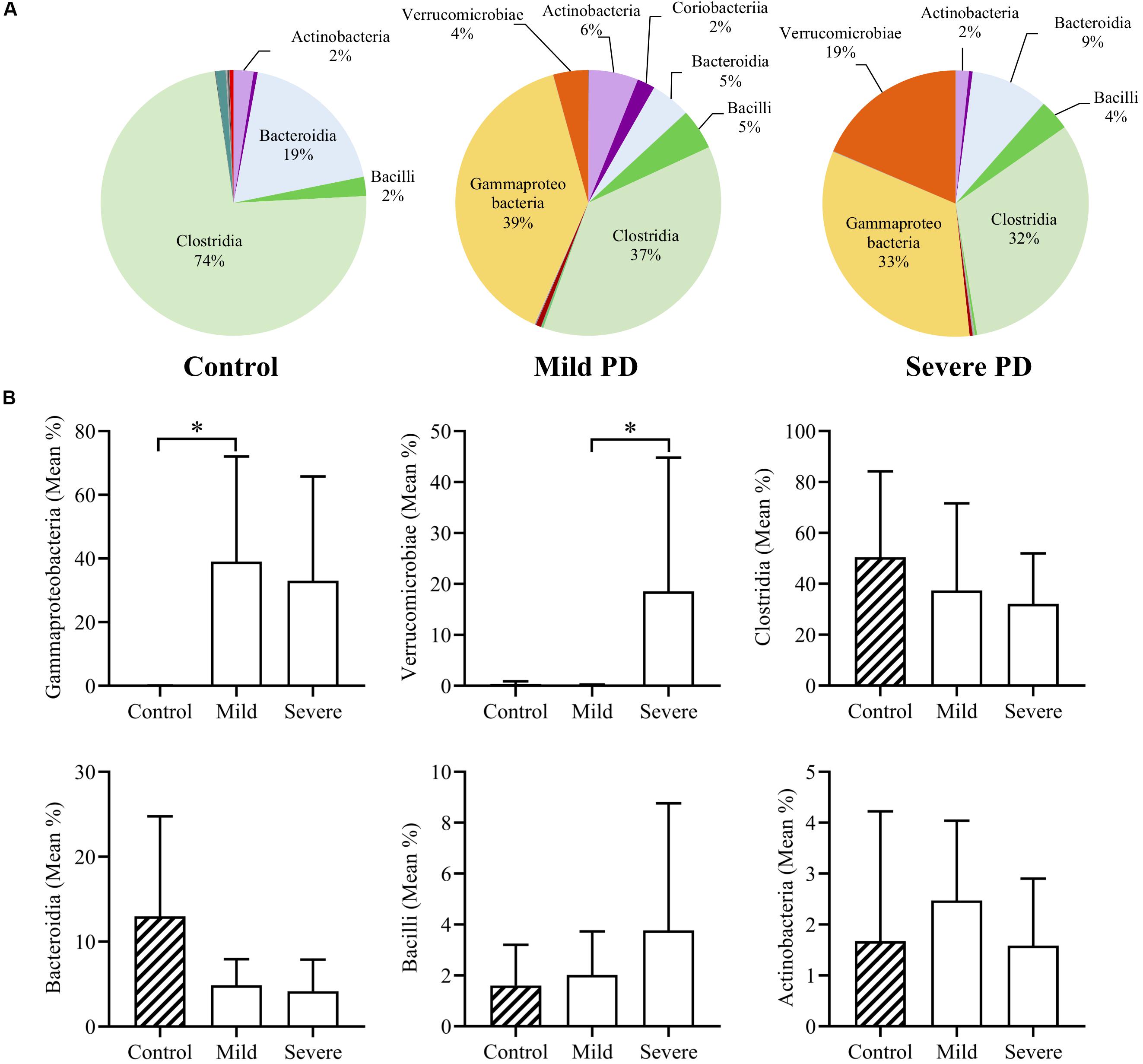
Frontiers | Altered Gut Microbiome in Parkinson's Disease and the Influence of Lipopolysaccharide in a Human α-Synuclein Over-Expressing Mouse Model
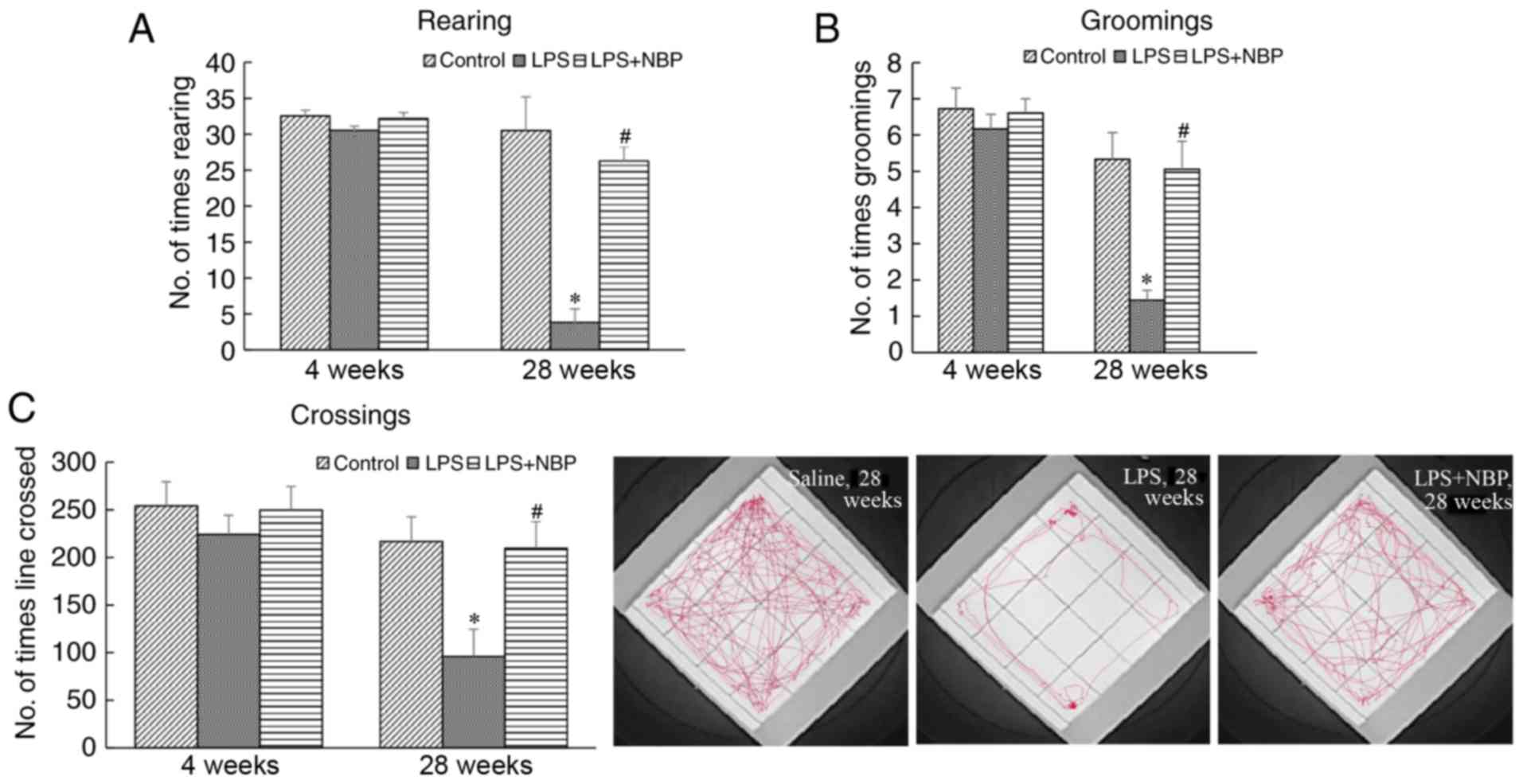
DL‑3‑n‑butylphthalide reduces microglial activation in lipopolysaccharide‑induced Parkinson's disease model mice
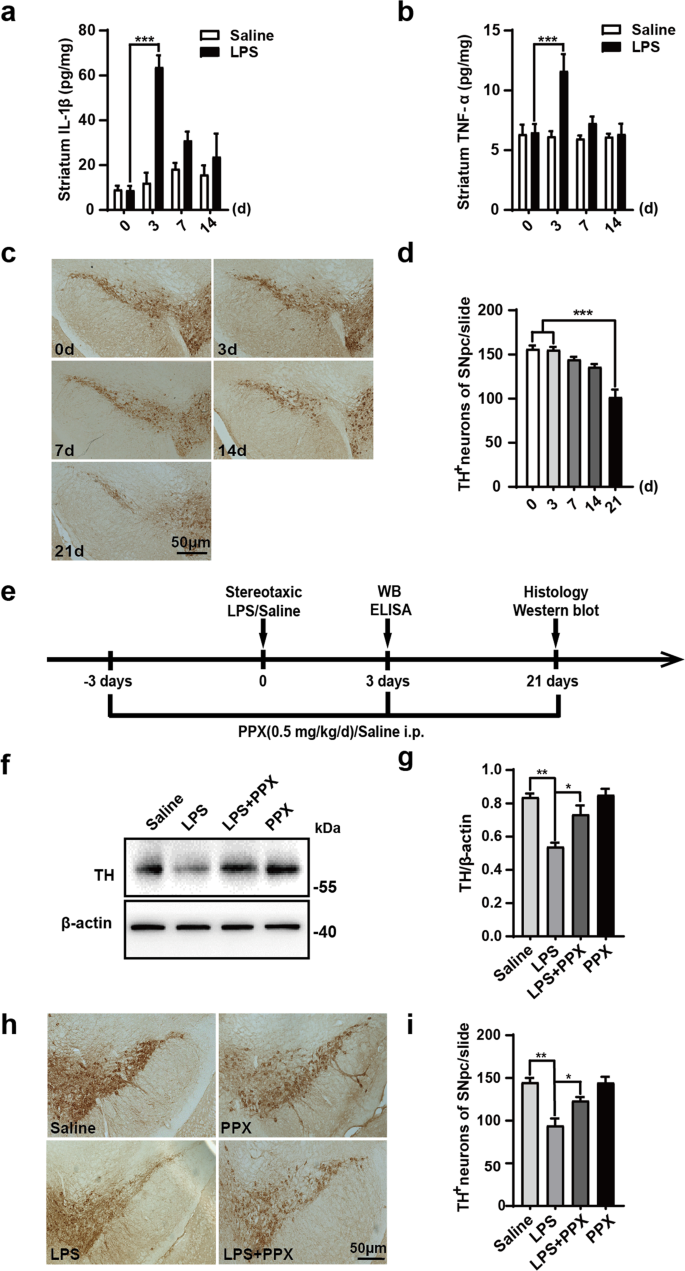
Pramipexole inhibits astrocytic NLRP3 inflammasome activation via Drd3-dependent autophagy in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease | Acta Pharmacologica Sinica
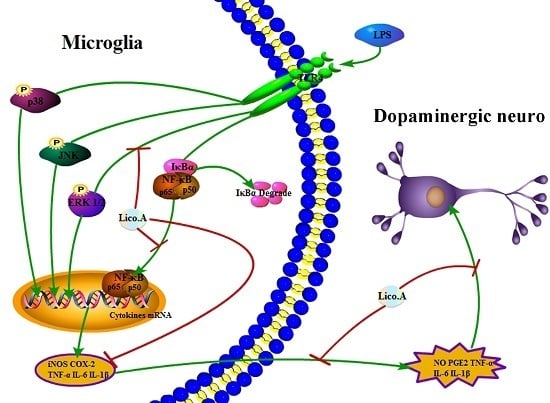
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Licochalcone A Prevents the Loss of Dopaminergic Neurons by Inhibiting Microglial Activation in Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Parkinson's Disease Models

Lipopolysaccharide animal models of Parkinson's disease: Recent progress and relevance to clinical disease - ScienceDirect

MicroRNA‐3473b regulates the expression of TREM2/ULK1 and inhibits autophagy in inflammatory pathogenesis of Parkinson disease - Lv - 2021 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library

Lipopolysaccharide animal models of Parkinson's disease: Recent progress and relevance to clinical disease | Semantic Scholar

Lipopolysaccharide animal models of Parkinson's disease: Recent progress and relevance to clinical disease - ScienceDirect

Inflammatory Animal Model for Parkinson's Disease: The Intranigral Injection of LPS Induced the Inflammatory Process along with the Selective Degeneration of Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons

PDF) Inflammatory Animal Model for Parkinson's Disease: The Intranigral Injection of LPS Induced the Inflammatory Process along with the Selective Degeneration of Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons
Intranasal LPS-Mediated Parkinson's Model Challenges the Pathogenesis of Nasal Cavity and Environmental Toxins | PLOS ONE

Neuroprotective Effect of Swertiamarin in a Rotenone Model of Parkinson's Disease: Role of Neuroinflammation and Alpha-Synuclein Accumulation | ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science

Parkinson's disease: Are gut microbes involved? | American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology

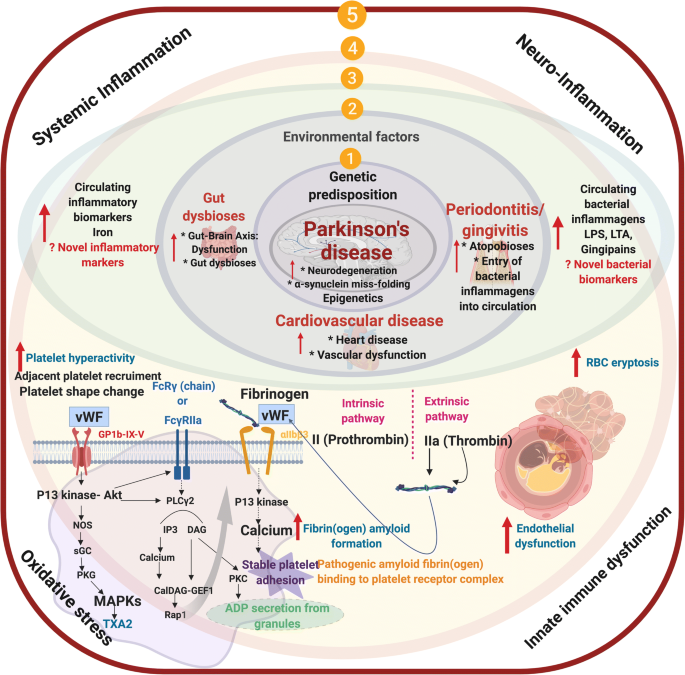
Parkinson's disease: a systemic inflammatory disease accompanied by bacterial inflammagens | bioRxiv

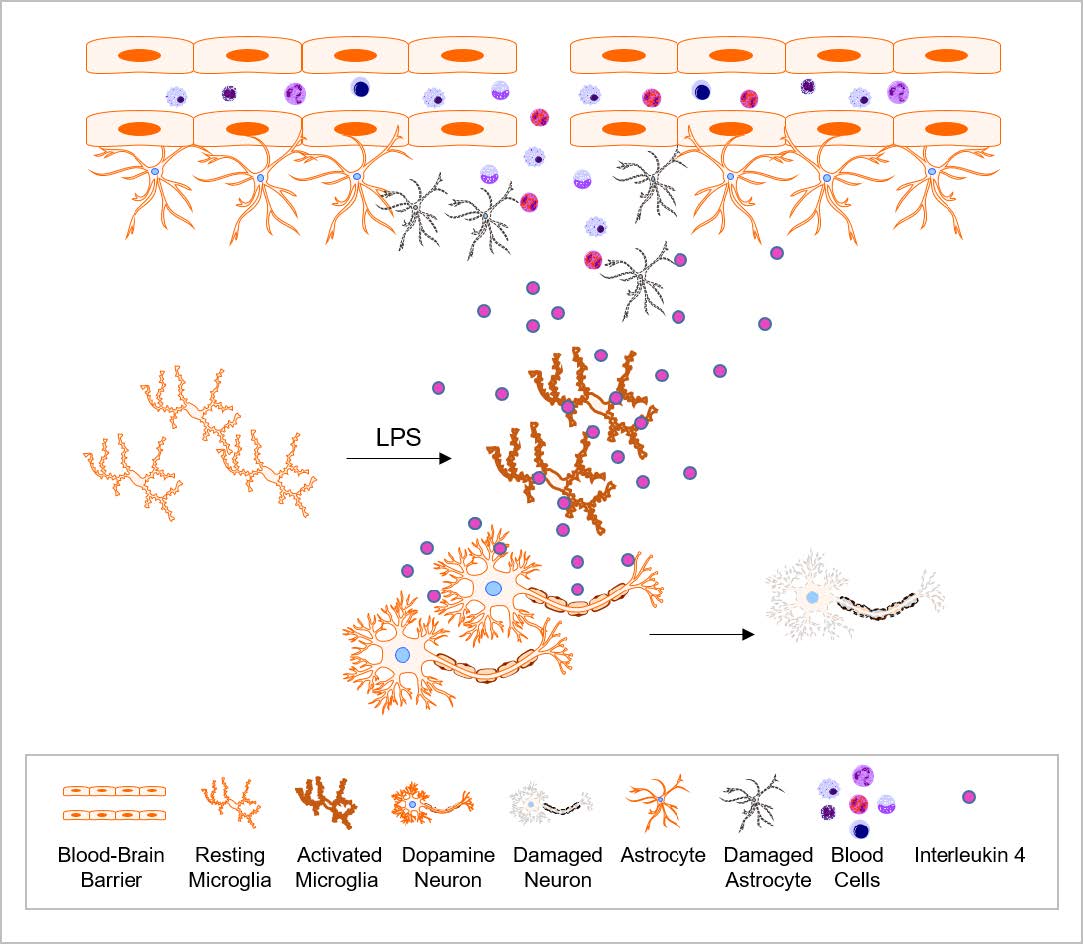


![PDF] Lipopolysaccharide Animal Models for Parkinson's Disease | Semantic Scholar PDF] Lipopolysaccharide Animal Models for Parkinson's Disease | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/a63c762e0fa3c8d5b24bb90bbf75a3ae3fff0174/6-Figure1-1.png)