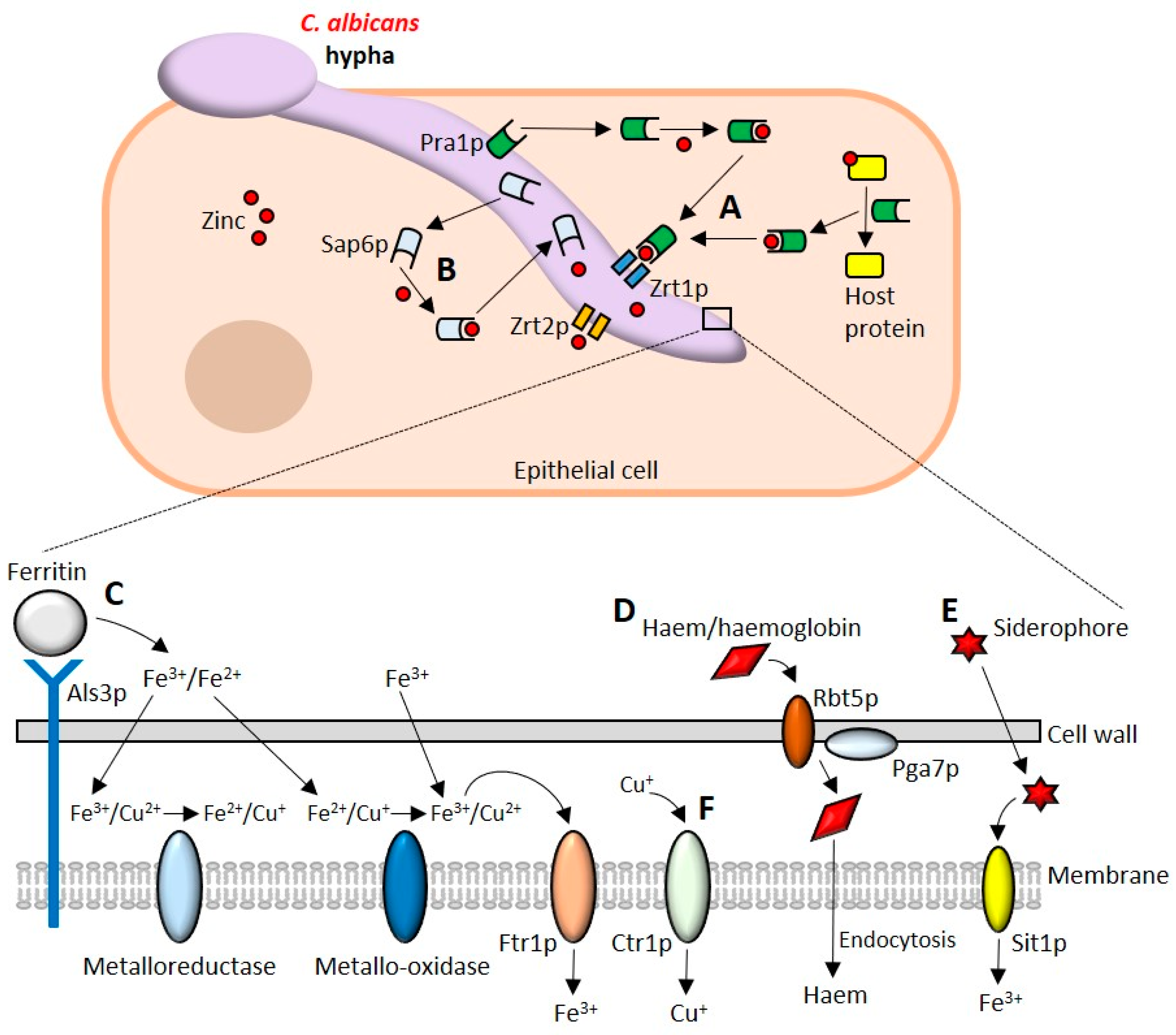
Pathogens | Free Full-Text | Candida albicans Interactions with Mucosal Surfaces during Health and Disease

Cellular interactions of Candida albicans with human oral epithelial cells and enterocytes - Dalle - 2010 - Cellular Microbiology - Wiley Online Library

Cytokine activation and cell damage by different Candida species and S.... | Download Scientific Diagram

Cytokine induction by C. albicans Dals mutants. C. albicans yeasts were... | Download Scientific Diagram

Oral epithelial cells orchestrate innate type 17 responses to Candida albicans through the virulence factor candidalysin | Science Immunology
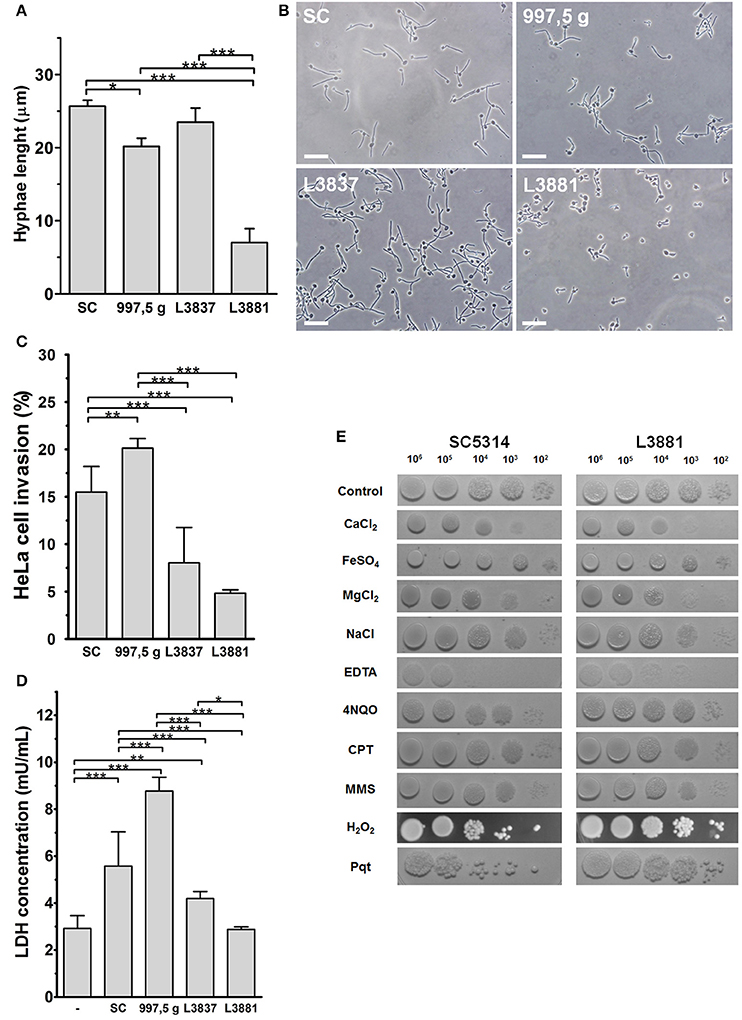
Frontiers | Candida albicans: The Ability to Invade Epithelial Cells and Survive under Oxidative Stress Is Unlinked to Hyphal Length
PDF) Evaluation of the Role of Candida albicans Agglutinin-Like Sequence (Als) Proteins in Human Oral Epithelial Cell Interactions

The Candida albicans toxin candidalysin mediates distinct epithelial inflammatory responses through p38 and EGFR-ERK pathways | Science Signaling

The Candida albicans toxin candidalysin mediates distinct epithelial inflammatory responses through p38 and EGFR-ERK pathways | Science Signaling
C. albicans Infection of TR146 Epithelial Cells Activates NF-κB and... | Download Scientific Diagram

PDF) Activation of MAPK/c-Fos induced responses in oral epithelial cells is specific to Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis hyphae | David Moyes - Academia.edu
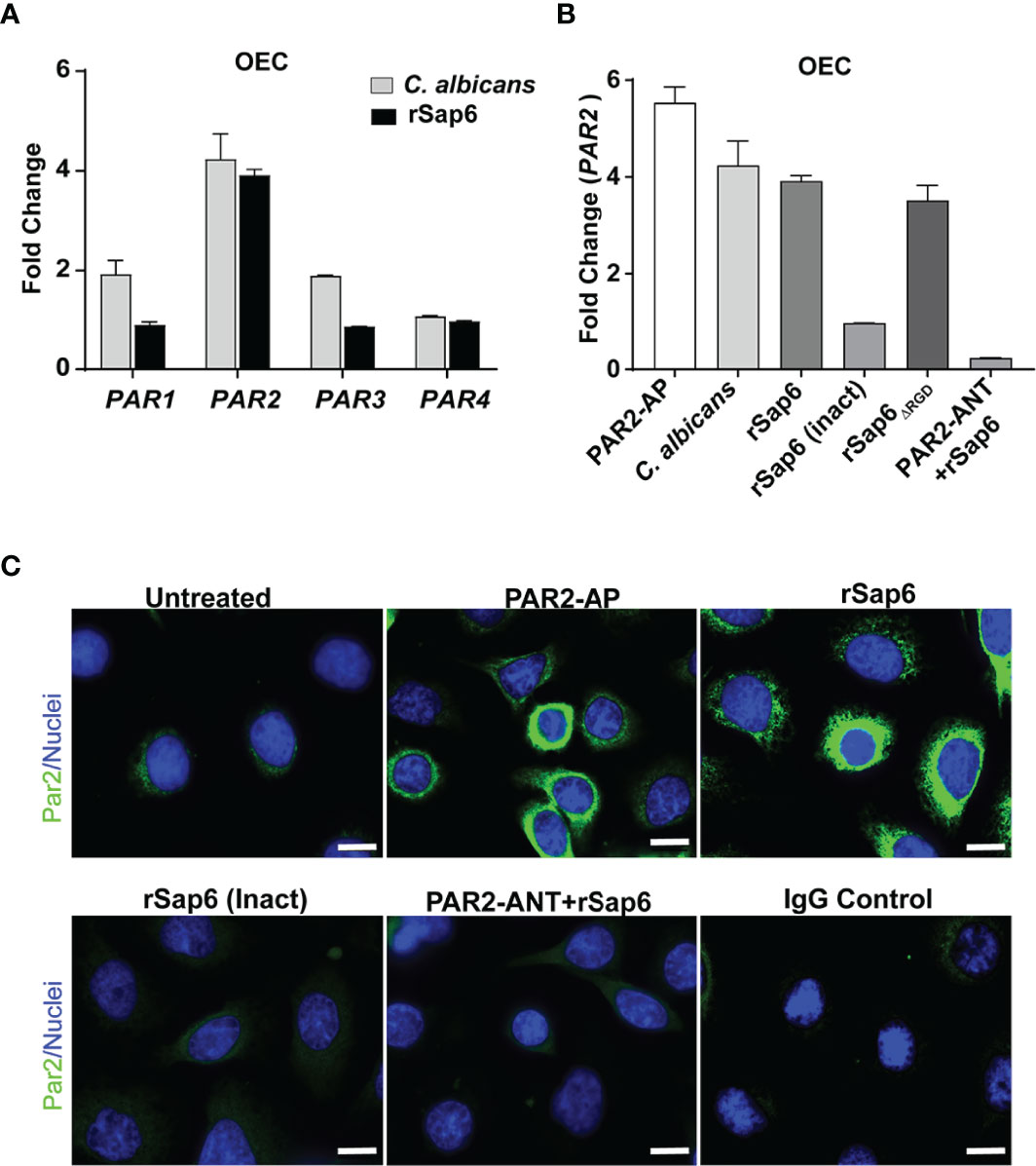
Frontiers | Candida albicans Sap6 Initiates Oral Mucosal Inflammation via the Protease Activated Receptor PAR2

Oral epithelial cells orchestrate innate type 17 responses to Candida albicans through the virulence factor candidalysin. - Abstract - Europe PMC
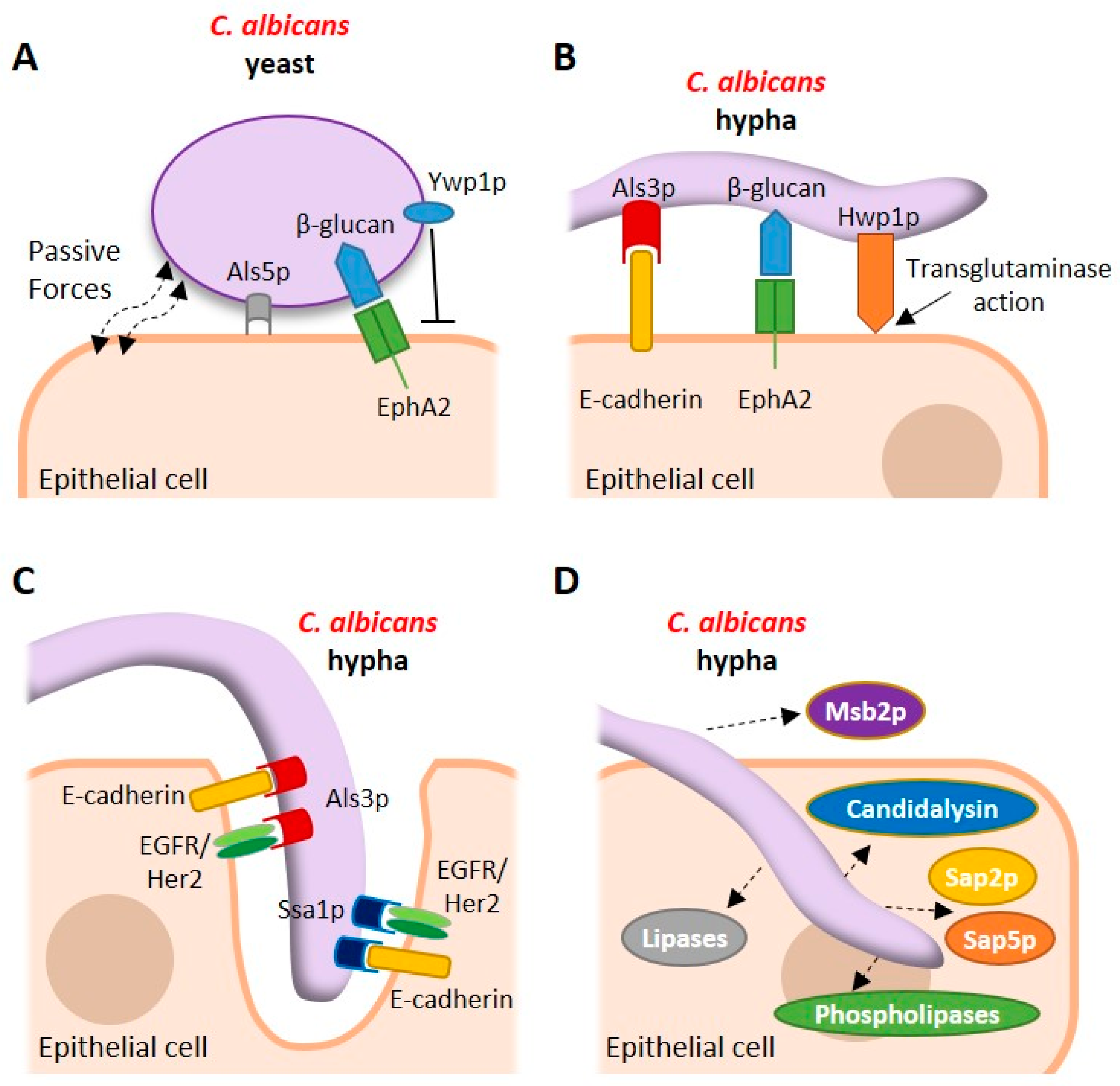
Pathogens | Free Full-Text | Candida albicans Interactions with Mucosal Surfaces during Health and Disease
From Attachment to Damage: Defined Genes of Candida albicans Mediate Adhesion, Invasion and Damage during Interaction with Oral Epithelial Cells | PLOS ONE

Cellular interactions of Candida albicans with human oral epithelial cells and enterocytes - Dalle - 2010 - Cellular Microbiology - Wiley Online Library
Candida albicans commensalism in the oral mucosa is favoured by limited virulence and metabolic adaptation | PLOS Pathogens
From Attachment to Damage: Defined Genes of Candida albicans Mediate Adhesion, Invasion and Damage during Interaction with Oral Epithelial Cells | PLOS ONE
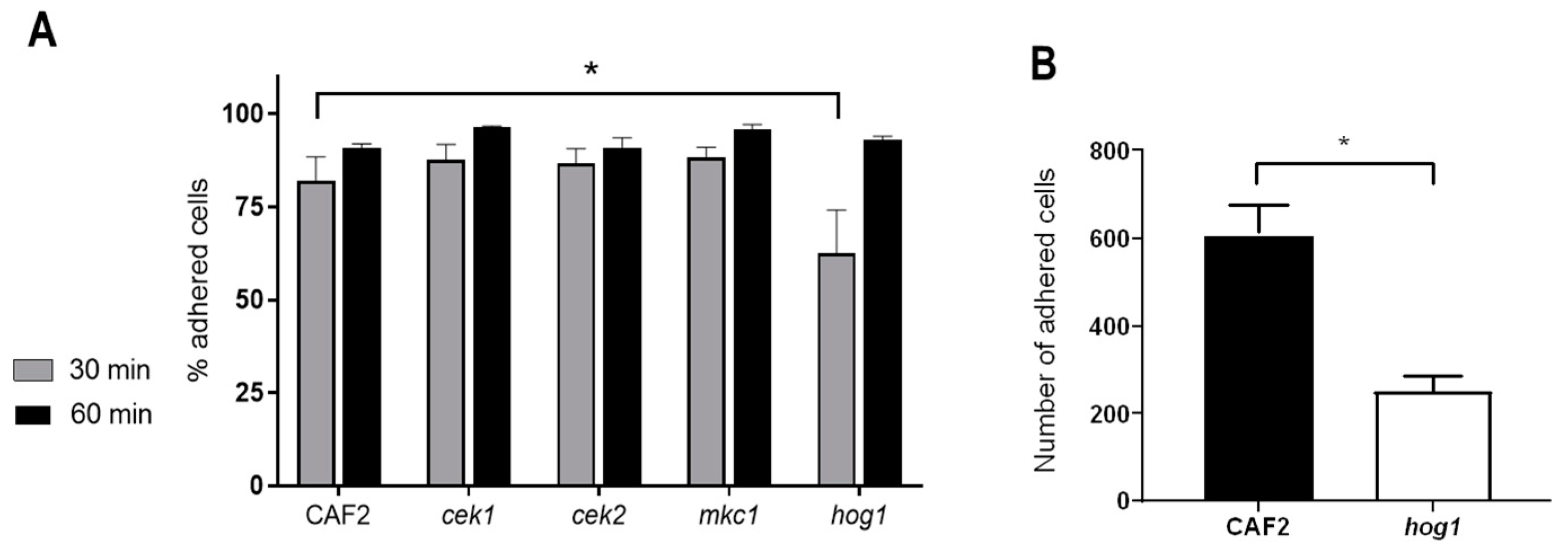
Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Cooperative Role of MAPK Pathways in the Interaction of Candida albicans with the Host Epithelium
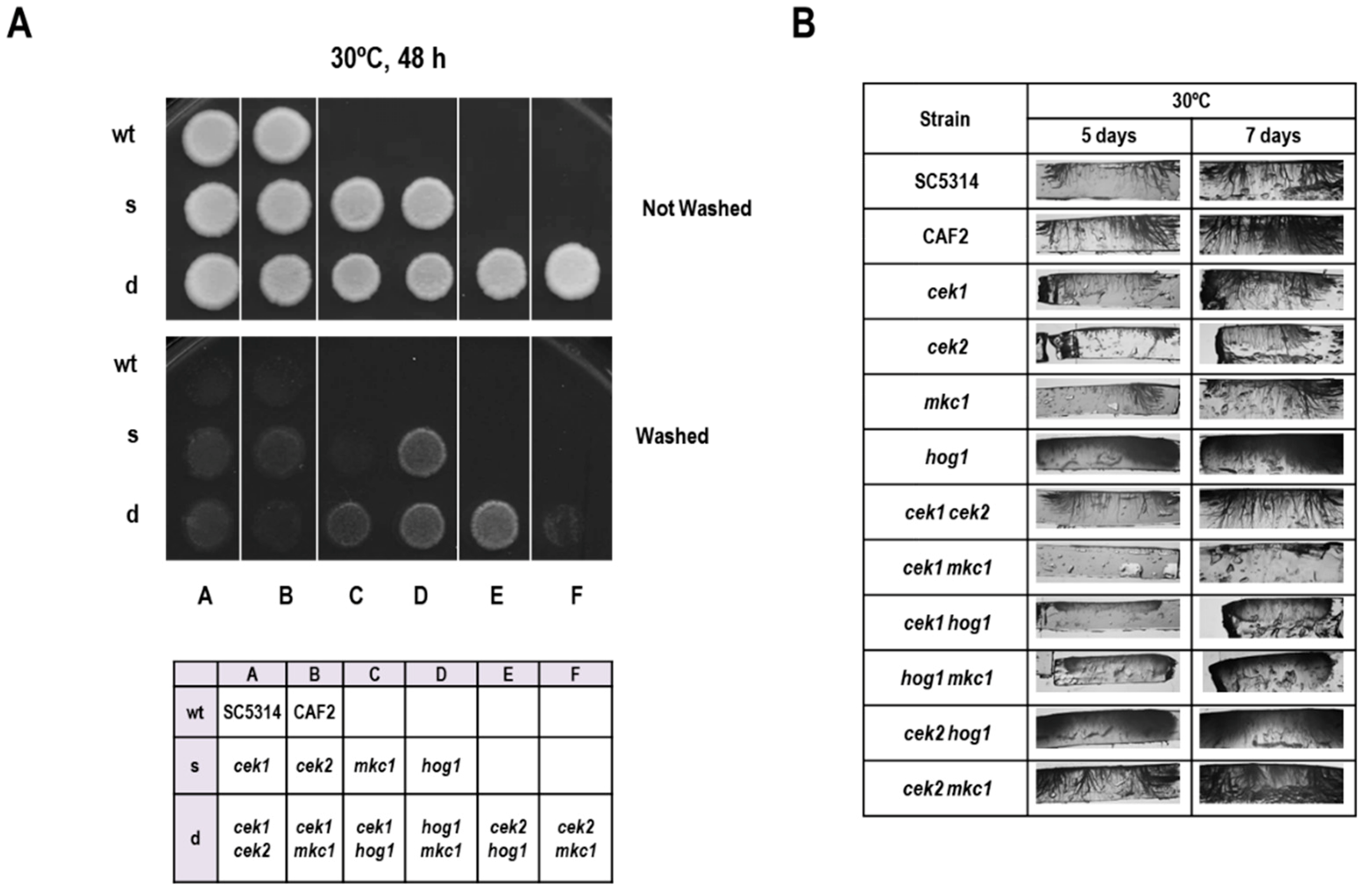
Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Cooperative Role of MAPK Pathways in the Interaction of Candida albicans with the Host Epithelium




